Research
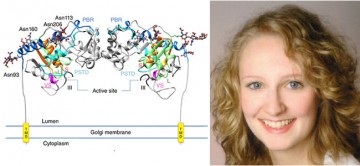
Insight into tumor metastasis: inner workings of the sialyltransferases
August 13, 2015
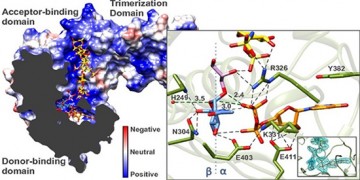
Modification of NCAM with polySia promotes migration of cells, a process that is critical for both the development of the embryonic brain and neural plasticity of the adult brain. Interestingly, elevated levels of polySia have been implicated in the malignant potential of tumors, tumor metastasis and poor clinical prognosis.
Striking a balance between blood product quality and safety
July 3, 2015
Dr. Peter Schubert, a Research Associate and Manager of Dr. Dana Devine’s Laboratory at CBR, collaborated with an industry partner, TerumoBCT, to investigate the impact of pathogen inactivation technologies in whole blood, as opposed to standard practice of individual blood components.
Taming antimicrobial peptides for treating bacterial infections
June 25, 2015
A toxic antimicrobial compound secreted by an Australian growling grass frog, Litoria raniformis, can prove useful against antibiotic resistant bacteria. The Kizhakkedathu group at CBR undertook this quest in their recent paper published in Biomacromolecules.
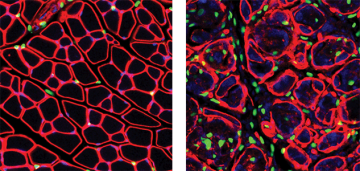
Dr. Rossi’s team discovers new mechanisms to target muscular dystrophy
June 8, 2015
Researchers unraveled a mechanism governing the deregulation of connective tissue cells (FAPs) after muscle injury. The interaction between FAPs and Macrophages could be a target of the new anti-fibrosis therapies.
Picornaviruses cleave host’s proteins to facilitate viral infection: Drs. Overall and Jan identify novel targets
May 21, 2015
Although initially viewed as ”collateral damage” resulting from viral replication cleavages in host proteins have increasingly been recognized as specific, targeted events aimed at impeding antiviral responses and facilitating viral infection.
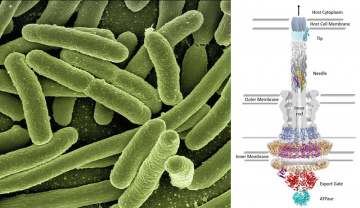
Clearing the path for infection: E. coli Type III Secretion System
May 14, 2015
It is fascinating to behold the ingenuity by which certain bacteria achieve infection in their host. One clear example is the enteropathogenic Escherichia coli, which uses a molecular syringe and needle complex to inject its virulence proteins into the cytoplasm of host intestinal epithelial cells.
Kizhakkedathu and Withers Make Breakthrough in the Pursuit of Universal Blood
May 6, 2015
A collaborating team of CBR and UBC Chemistry scientists described the development of an improved enzyme that takes us a step closer to achieving universal blood.
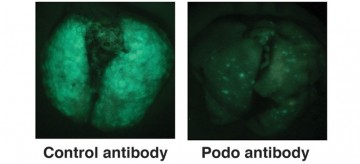
Kelly McNagny group developed an antibody to target the spread of aggressive tumors
April 13, 2015
Recently published in Breast Cancer Research, study showed how inhibiting podocalyxin, a protein marker found in many highly aggressive tumours, dramatically slowed the metastasis
Bromme lab discovers collagen degradation mechanisms – potential targets for osteoporosis?
April 8, 2015
This research not only provides understanding of how cathepsin K breaks down collagen fibers but also opens the door for the design of a new class of drugs selectively targeting the degradation of collagen through cathepsin K.
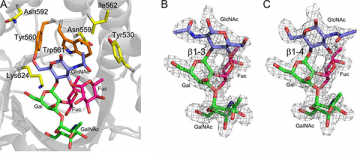
Deciphering the ‘Glycocode’ of methicillin resistant S. aureus
April 2, 2015
It is clear that the ‘glycocode’ (complex glycosylation process) plays a vital role in bacterial survival and pathogenicity. The authors believe that TarM and TarS would be ‘lucrative targets for novel therapeutic agents in light of an ever-decreasing antibiotic arsenal’.