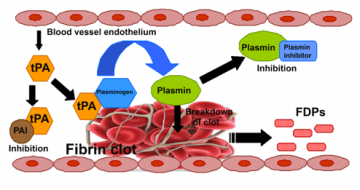
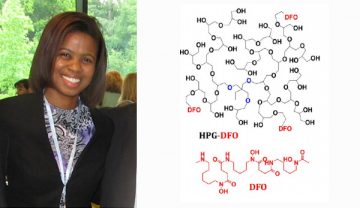
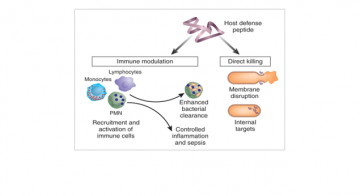
Dr. Scott Modifies Red Blood Cells to Make Transfusion Possible in Patients with Rare Blood Types
When a person is in dire need of blood, a blood transfusion seems like a simple solution. A donor donates blood, and eventually a patient in need receives it. Yet, in reality this life-saving medical procedure, as safe as it may be, is not that simple.