Research
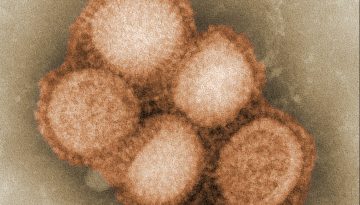
Host Tissue Factor on the Virus Envelope – A New Antiviral Target?
February 27, 2020
Viruses are small genetic bundles that hijack the metabolic processes of infected cells and can make us sick. One type of virus, called “enveloped viruses”, includes influenza, human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and herpes simplex virus 1 (HSV-1).
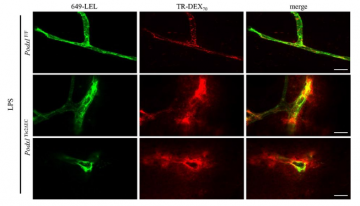
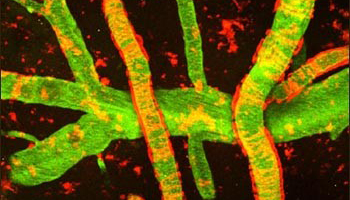
A new player in blood-brain-barrier integrity
February 6, 2020
Podocalyxin (Podxl) is a protein primarily expressed on the inner surface of blood vessels and specialized kidney cells called podocytes. Although Podxl plays a critical role in kidney development and function, its purpose in blood vessels has remained cryptic.
Metaling with Chelation Therapy: Reducing Transfusion-Associated Iron Toxicity with Conjugated Drugs
August 29, 2019
Beta-thalassemias are a group of inherited blood disorders caused by a decrease in beta hemoglobin chains that can result in severe anemia, reduced oxygen supply to tissues, failure to thrive, and death.
Dampening the Inflammatory Response to P. aeruginosa Infection using a Synthetic Immunomodulatory Peptide
July 25, 2019
Antibiotic resistance and the lack of novel antibiotics pose a real threat to health, and therefore new solutions to fight resistant bacteria are required.
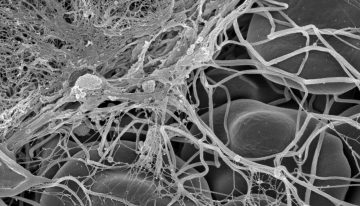
Self-propelled Hemostatic Particles Find a New Home in Gauze and Spray Cartridges
July 11, 2019
Self-propelled particles—What started as a “wouldn’t that be cool” idea has become a real technology that has gained the support of many groups that hope to some day see this product, on the front of both military and civilian lines, saving lives.
Walking the Tightrope
May 23, 2019
Imagine, you are walking on a tightrope. If you fall to one side of this narrow line, zombies are waiting to eat you up. On the other side, it is a fall into a crazy deep canyon.
Can Dysfunctional Clotting Contribute to Neurological Disorders?
April 4, 2019
Alzheimer’s disease is a devastating neurological disorder with no known cure. Characterized by gradual cognitive decline, its effects are felt throughout Canada. Over half a million Canadians are living with dementia, and Alzheimer’s disease is a major contributor to this number.
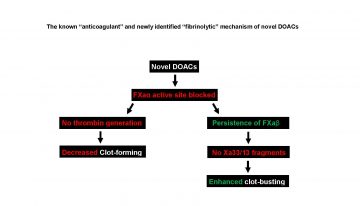
New Anticoagulants Enhance “Clot-busting” Ability of the “Clot-former” Factor Xa
March 28, 2019
If you, loved ones or friends suffer from diseases that may involve abnormal blood clotting, such as heart attack, stroke, atherosclerosis, deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism or even cancer, commercials on “blood thinners” (anticoagulants) may catch your attention more than other drugs while watching your favourite TV show.
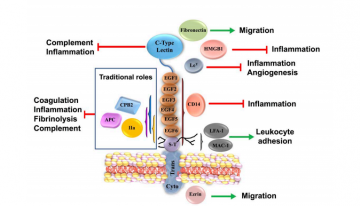
Thrombomodulin: Old Protein with New Functions and Hope
January 31, 2019
As its name suggests, thrombomodulin (TM) modulates thrombin activity. The traditional role of TM is to vastly accelerate production of activated protein C from its zymogen by thrombin.
From Computers to Clinics: Advances in Designing Polyphosphate Inhibitors as Novel Anti-thrombotics
January 10, 2019
Thrombosis, the formation of a potentially deadly blood clot, remains one of the leading causes of death and disability worldwide. Once formed, clots can slow or obstruct normal blood flow, leading to damage to surrounding tissue.